In the ever-evolving landscape of manufacturing, Automatical Welding has emerged as a transformative technology that is redefining production efficiency and quality. According to Dr. Helen Carter, a leading expert in the field of automatical welding, "The integration of automation in welding processes not only enhances precision but also significantly reduces the overall production time." Her insights underscore the importance of mastering these techniques as industries strive for competitiveness and innovation.
As we look toward the future, particularly in 2025, it becomes imperative for professionals in the welding industry to familiarize themselves with the latest advancements in automatical welding. Innovations such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and robotic welding systems are reshaping traditional welding practices, making them faster and more reliable. The guide that follows aims to provide a comprehensive overview of these techniques and innovations, ensuring that welders and manufacturing professionals are well-equipped to adapt to this rapid evolution.
Understanding and mastering automatical welding is not merely an option; it is a necessity for those seeking to thrive in this high-tech industrial environment. This guide will serve as a valuable resource, outlining key strategies, tools, and innovations that will empower professionals to excel in automatical welding and secure their place in the future of manufacturing.

Automatic welding techniques have transformed the landscape of industrial manufacturing by increasing efficiency, consistency, and quality in welding operations. This introduction delves into the fundamentals of automatic welding, which employs advanced machinery and robotics to perform welding tasks with minimal human intervention. The key advantage of this approach lies in its ability to execute repetitive welding processes with precision, thus reducing the chances of human error and enhancing production rates.
Innovation plays a crucial role in the evolution of automatic welding. With advancements in technology, new techniques such as laser welding, arc welding automation, and adaptive control systems have emerged. These innovations not only improve the welding quality but also expand the range of applications across various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and construction. As these technologies continue to evolve, they present exciting opportunities for welders and engineers to enhance their skill sets and adapt to the changing demands of the market. Embracing these advancements ensures that professionals remain at the forefront of welding technology, ready to tackle the challenges of modern manufacturing.
This chart illustrates the advancement of automatic welding techniques and their adoption rates over the years. The data reflects the percentage of welding firms utilizing these techniques, highlighting the growing trend in the industry.
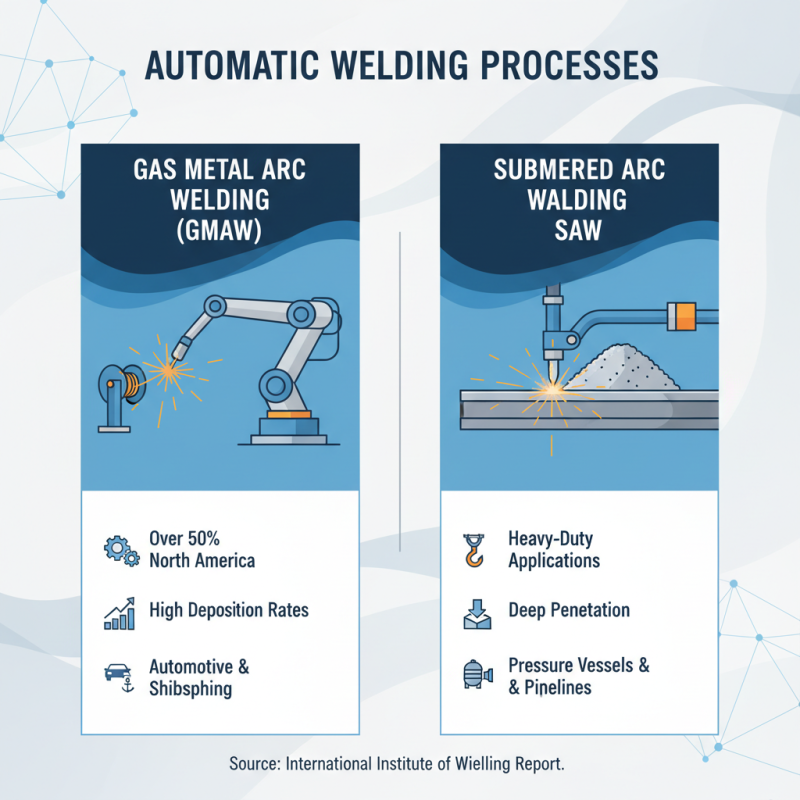
Automatic welding has become a cornerstone of modern fabrication, boasting numerous processes tailored to specific applications. Among these, Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW) and Submerged Arc Welding (SAW) stand out for their precision and efficiency. According to a report from the International Institute of Welding, GMAW accounts for over 50% of welding processes utilized in North America due to its adaptability across various materials. Its ability to provide high deposition rates while maintaining quality makes it ideal for industries such as automotive and shipbuilding. On the other hand, Submerged Arc Welding is well-regarded in heavy-duty applications like pressure vessels and pipelines, as it allows for deep penetration and reduced slag.
When exploring automatic welding techniques, understanding the key types is essential for optimizing production. For instance, Flux-Cored Arc Welding (FCAW) is particularly beneficial in outdoor environments, where it outperforms other methods by reducing the sensitivity to wind. The American Welding Society cites that FCAW can achieve welding speeds of up to 50% higher than traditional methods, making it a preferred choice for construction and structural applications.
**Tips:** When selecting an automatic welding process, consider the material type and thickness, as well as the operational environment. Choosing the right technique not only enhances weld quality but also improves overall productivity. Additionally, invest in proper training for your workforce; experts suggest that skilled operators can increase efficiency by nearly 30% through effective technique implementation.
Automatic welding has revolutionized the manufacturing and construction industries, driven by advancements in technology and equipment. Mastering this technique requires a solid understanding of essential tools such as robotic welders, advanced welding machines, and real-time monitoring systems. According to a report by the International Institute of Welding, the adoption of automatic welding technologies can improve production efficiency by 30-50% while significantly reducing labor costs. This underscores the importance of investing in the right equipment to stay competitive in the ever-evolving market.
To excel in automatic welding, it's crucial to leverage innovations such as artificial intelligence and machine learning for process optimization. These technologies enhance quality control by enabling real-time adjustments based on welding parameters, thereby minimizing defects and rework. A recent study by the American Welding Society highlights that implementing automated systems can decrease error rates by up to 40%, emphasizing the impact of incorporating modern technology in welding processes.
**Tips:** When selecting equipment for automatic welding, prioritize versatility and ease of integration with existing systems. Training your workforce on new technologies will maximize their potential and ensure smooth operations. Regular maintenance of machinery is also indispensable, as it significantly affects performance and longevity, leading to higher productivity in the long run.
| Technique | Description | Essential Equipment | Expected Innovations |
|---|---|---|---|
| TIG Welding | A precise welding technique that uses a non-consumable tungsten electrode. | TIG Welder, Argon Gas Supply | Improved automation for better weld quality |
| MIG Welding | Uses a continuously fed wire as an electrode and a shielding gas. | MIG Welder, Gas Cylinder, Welding Wire | Integration of AI for adaptive welding processes |
| Laser Welding | Utilizes a laser beam to achieve deep penetration welds. | Laser Welder, CNC System | Nanosecond pulse technology for improved control |
| Plasma Arc Welding | Uses a plasma torch to melt and join materials. | Plasma Welder, Shielding Gas Equipment | Development of portable plasma welders |
| Flux-Cored Arc Welding | An alternative to MIG welding that uses a tubular wire filled with flux. | Flux-Cored Welder, Flux-Cored Wire | Automatic feeders for continuous wire supply |
Safety practices and quality control are crucial components in mastering automatic welding techniques. One of the primary safety practices involves the proper use of personal protective equipment (PPE). Welders must wear appropriate gear, including helmets with proper shading, gloves, and flame-resistant clothing, to shield themselves from harmful sparks and UV radiation. Additionally, it's imperative to maintain a well-ventilated workspace to minimize exposure to toxic fumes and gases generated during the welding process. Regular safety training sessions can reinforce awareness and promote a culture of safety within welding teams.
Quality control in automatic welding hinges on rigorous inspection and testing methods to ensure weld integrity and consistency. Techniques such as ultrasonic testing and visual inspections are essential for detecting defects that could compromise the strength of the weld. Establishing standardized procedures for weld preparation, execution, and post-weld treatment further bolsters quality assurance. Furthermore, implementing continuous monitoring systems during the welding process can provide real-time data on critical parameters, enabling immediate adjustments and ensuring high-quality results.
Emphasizing both safety practices and robust quality control measures can significantly enhance the effectiveness and reliability of automatic welding operations.
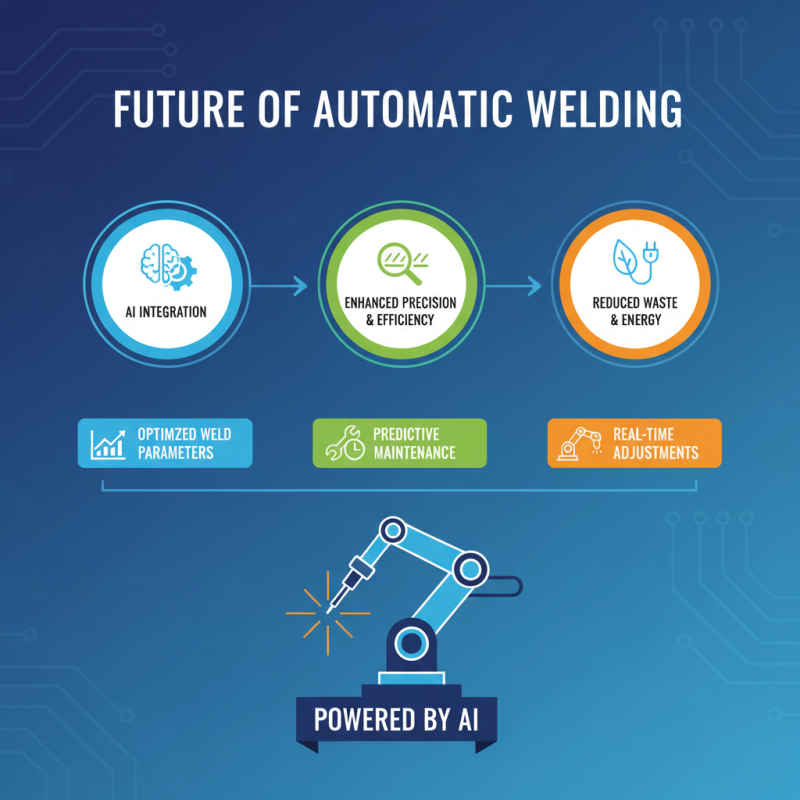
The future of automatic welding technology is poised for remarkable advancements that promise to enhance efficiency and precision across various industries. One of the most significant trends is the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) into automatic welding systems. AI algorithms can analyze real-time data to optimize welding parameters, predict maintenance needs, and even adjust settings on the fly. This not only improves the quality of welds but also reduces waste and energy consumption, making processes more sustainable.
As automation continues to evolve, collaboration between robots and human workers will become more seamless. Innovations such as augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) are set to revolutionize training and operational protocols. For example, AR can provide real-time guidance for technicians during weld inspections, while VR training modules can simulate complex welding scenarios, enabling workers to hone their skills in a safe environment.
**Tips for Mastering Automatic Welding:**
- Stay updated on the latest technologies in AI and automation to leverage their capabilities in your welding processes.
- Invest time in training with AR and VR tools to enhance your understanding and practical skills in automatic welding.
- Establish a regular maintenance schedule for your equipment to ensure optimal performance and longevity, reducing downtime and costly repairs.