In the rapidly evolving industrial landscape, mastering Automatical Welding techniques is pivotal for achieving efficiency in production. As the demand for precision and speed increases, professionals in the field must adapt and refine their skills. Dr. Michael Johnson, a leading expert in automatical welding technology, once stated, "The future of manufacturing lies in our ability to integrate automation seamlessly into our welding processes." This insight underscores the importance of staying abreast of innovative technologies that enhance production capabilities.
The increasing complexity of manufacturing tasks necessitates a profound understanding of Automatical Welding systems and their applications. As companies strive to reduce costs while improving quality, automating welding operations provides a solution that meets these demands. Understanding the principles of automatical welding not only leads to greater productivity but also ensures consistent results that meet stringent industry standards.
In this outline, we will delve into key strategies for mastering automatical welding techniques, examining their impact on production efficiency and overall operational excellence. Embracing these advancements will equip professionals with the necessary tools to thrive in an increasingly competitive market.

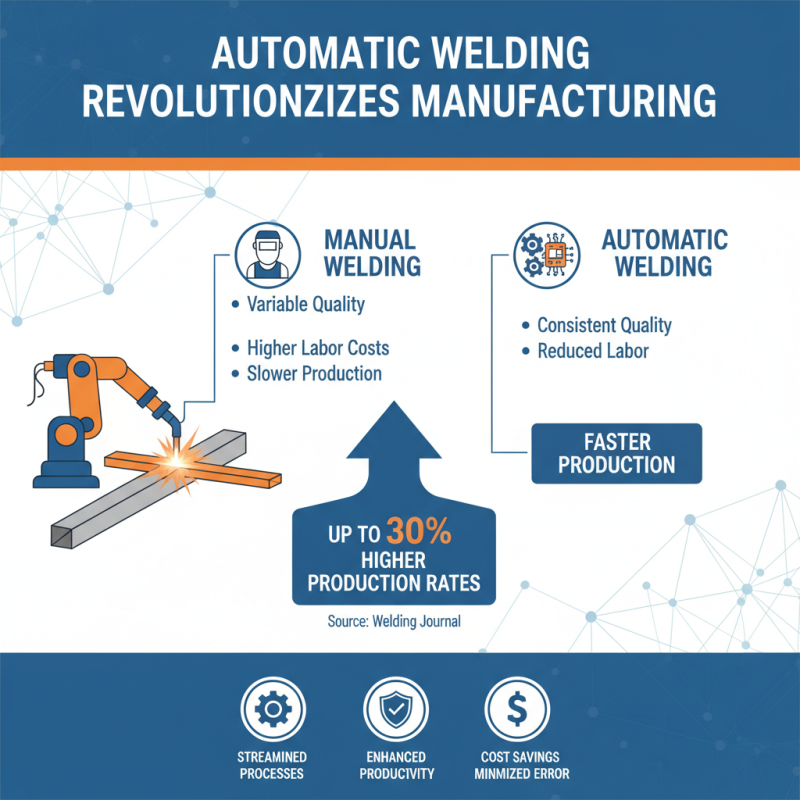
Automatic welding techniques have revolutionized the manufacturing industry, streamlining processes and enhancing productivity. At its core, automatic welding employs mechanized systems that utilize pre-programmed instructions to perform welding tasks with precision. According to the Welding Journal, companies that implement automatic welding can achieve up to 30% higher production rates compared to manual welding methods. This increase in efficiency not only reduces labor costs but also minimizes the risk of human error, resulting in more consistent weld quality.
To get started with automatic welding, it is essential to understand the basic principles, including the types of welding processes—such as Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW) and Tungsten Inert Gas (TIG) welding—that can be automated. Additionally, mastering the setup of welding parameters and configurations is crucial for successful operation. As highlighted in a report by the American Welding Society, an investment in training for skilled personnel in these technologies can yield a return on investment within the first year of implementation.
Tips: When transitioning to automatic welding systems, ensure your equipment is compatible with existing workflows to prevent disruptions. Regular maintenance of the machinery is vital to maintaining optimal performance. Lastly, conducting trials with different materials can help fine-tune processes tailored to specific production needs, ultimately leading to enhanced output quality.
Automatic welding has revolutionized the manufacturing landscape, enabling companies to enhance productivity and streamline their operations. At the core of efficient automatic welding are key pieces of equipment and tools that ensure precision, speed, and consistency. One essential component is the robotic welding system, which offers flexibility and adaptability for various welding tasks. These systems are equipped with advanced sensors and controls that allow for real-time adjustments, resulting in high-quality welds with minimal human intervention.
In addition to robotic systems, companies should invest in specialized welding machines that cater to different materials and joint configurations. MIG, TIG, and submerging arc welding machines are just a few examples that can be essential for different production needs. Furthermore, welding positioners and fixtures play a crucial role in maintaining the stability of the workpieces during the welding process. By utilizing automated cutting and preparation tools, manufacturers can ensure that materials are ready for efficient welding, reducing downtime and increasing throughput. Together, these key tools create a robust infrastructure that supports automated welding processes, ultimately leading to enhanced production efficiency.
This chart illustrates the efficiency of various automatic welding techniques in terms of production speed and material compatibility. The data highlights the performance of different methods over a set period.
Implementing automatic welding in production processes requires a strategic approach to ensure efficiency and quality. The first essential step is to assess the current welding operations and identify areas where automation can be beneficial. According to a report by the American Welding Society, automated welding systems can increase production speed by up to 50%, significantly reducing labor costs and improving product consistency. This data highlights the importance of understanding the workflow and pinpointing tasks that can be automated to streamline operations.
Once potential applications for automation have been identified, the next step is selecting the appropriate technology for the specific welding tasks at hand. Key considerations include the type of welding method—such as MIG, TIG, or spot welding—and the materials involved. Industry studies indicate that around 60% of manufacturers who switch to automated welding report a notable reduction in defects and rework. Investing in training and upskilling employees to work alongside automated systems is crucial, as skilled operators can optimize the process further and troubleshoot any issues that arise during production.
Finally, implementing a phased rollout of the automated system allows for careful monitoring and adjustment. According to the International Institute of Welding, companies that adopt a gradual integration strategy experience less disruption and more substantial long-term gains in productivity. Regular assessments and feedback loops can help refine the automated processes and ensure the technology is fully leveraged to maximize production efficiency.
| Step | Process | Expected Outcome | Timeframe | Tools Required |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Conduct Initial Assessment | Identification of needs and specifications | 1 Week | Assessment tools, Worksheets |
| 2 | Choose Welding Equipment | Selection of appropriate machines | 2 Weeks | Research materials, Vendor contacts |
| 3 | Training of Personnel | Skilled operators for automatic welding | 3 Weeks | Training programs, Manuals |
| 4 | System Integration | Automation of existing workflows | 4 Weeks | Software, Integration tools |
| 5 | Testing and Feedback | Refinement of processes | 2 Weeks | Feedback forms, Testing gear |
Automatic welding techniques offer significant efficiencies in production, but they come with a set of challenges that can hinder optimal results. One common issue is the inconsistency in weld quality, which can arise from variations in material thickness, joint fit-up, and operator skill level. To mitigate this, it is essential to implement rigorous quality control measures and regular calibration of equipment. Training programs designed to enhance the skills of operators in understanding these variations can also contribute to improving weld consistency.
Another significant challenge is equipment malfunction, which can lead to production downtime and increased costs. Regular maintenance schedules and quick troubleshooting protocols can help minimize these disruptions. Employing predictive maintenance techniques, where data analytics are used to forecast equipment failures, allows for proactive interventions before issues escalate. Additionally, integrating advanced automation technologies can provide enhanced reliability and reduce human error, further ensuring smooth operational flow in automatic welding environments.

The field of automatic welding technology is evolving rapidly, driven by innovations that enhance production efficiency and precision. According to a report by Research and Markets, the global automated welding market is projected to reach approximately $6.02 billion by 2025, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 6% from 2021. This growth is largely attributed to the increasing demand for high-quality welding processes in industries such as construction, automotive, and aerospace, where reliability and speed are crucial.
Future trends in automatic welding technology include advancements in artificial intelligence and machine learning. These technologies are expected to enable welding systems to adapt in real-time to varying conditions, significantly reducing human intervention. For instance, a report from Grand View Research indicates that the integration of AI in manufacturing processes can lead to a 30% increase in efficiency. Additionally, innovations in welding equipment, like the implementation of collaborative robots (cobots), are set to transform the workforce dynamics, allowing machines to work safely alongside human welders and enhancing overall productivity. As the industry embraces these advancements, manufacturers must stay informed and adapt to remain competitive in this fast-paced environment.






