A Swing Welding Lathe is an essential tool in metalworking. It combines the functionality of welding and turning. This machine allows for intricate designs and precise joining of materials. Understanding its operation and applications can enhance productivity.
In the world of fabrication, a Swing Welding Lathe stands out. The lathe rotates components, while the welder applies heat. This process requires skill and attention to detail. However, it can sometimes lead to uneven welds. Observing common pitfalls is vital for improvement.
Many people overlook the versatility of a Swing Welding Lathe. It can work on various shapes and sizes, accommodating diverse projects. Yet, users often face challenges with setup and calibration. Reflecting on these experiences can lead to better outcomes. A focus on learning can transform mistakes into valuable lessons.
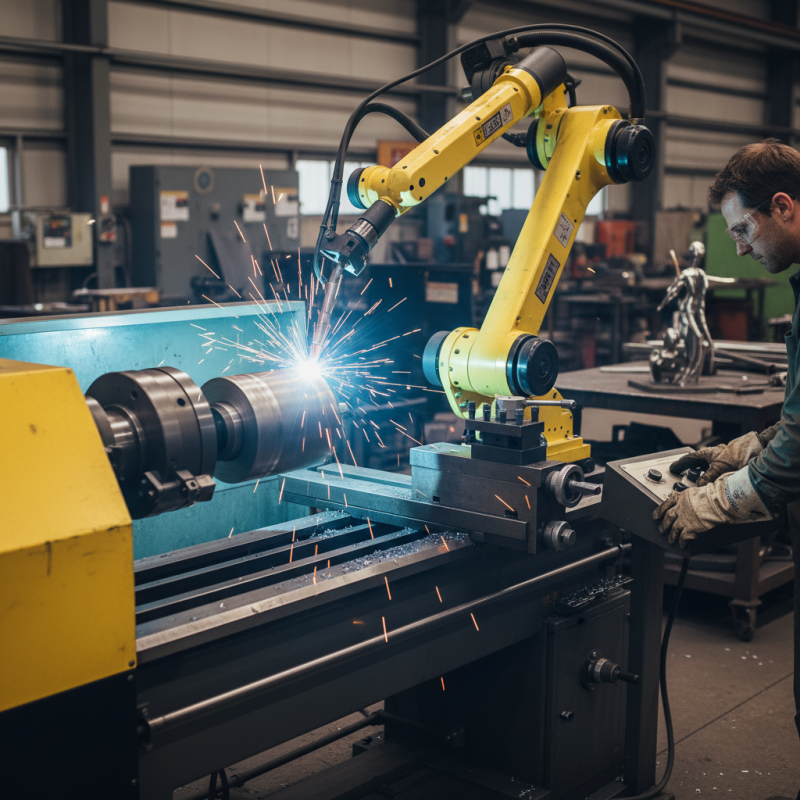

A swing welding lathe is an essential tool in metal fabrication. It combines lathe functions with welding capabilities. This machine allows for the manipulation of large workpieces by swinging the chuck. A report from the International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology highlights that these lathes can accommodate parts up to 20 feet in diameter. This versatility is crucial for industries like aerospace and shipbuilding.
The design of a swing welding lathe enhances efficiency. Operators can combine welding and turning processes. This integration minimizes downtime. In a recent study, manufacturers reported a 30% reduction in production time when using these lathes compared to separate machines. However, the complexity of the setup can pose challenges. Incorrect alignment may lead to subpar welds or uneven surfaces.
While swing welding lathes offer advanced capabilities, they also require skilled operators. Training is vital for maximizing their potential. Industry reports suggest that the lack of proper training leads to a 15% increase in errors. Regular maintenance is equally important. Neglect can affect machine performance and lifespan, resulting in costly repairs.
A swing welding lathe is a unique machine tool. It combines welding and turning processes. This allows for efficient fabrication of complex parts. Key components define its functionality.
The bed is the foundation, supporting all components. It provides stability during operations. The swing arm is another crucial part. It holds the workpiece securely while the welding torch moves. This arm pivots, allowing access to different angles. Then, there’s the feed system. It ensures a precise movement of the workpiece.
Welding controls manage the heat and speed. These controls help in adjusting parameters for various materials. However, calibrating these controls can be tricky. A slight miscalibration can lead to poor welds. Regular maintenance is essential, yet often overlooked. Operators need to examine wear and tear regularly.
A swing welding lathe is a unique machine designed for metalworking. It combines features of both a lathe and a welding apparatus. The main purpose is to create or repair cylindrical metal parts. Operators position the workpiece on the lathe, allowing for precise welding in a controlled environment. This setup enhances the stability of the metal while welding.
The lathe operates with a rotating worktable. The workpiece spins, while the welding torch moves across it. This allows for even heat distribution. However, achieving the perfect weld can be challenging. Many factors affect the outcome, such as speed and angle. If these aren’t just right, the weld may not be strong enough.
Safety is crucial when using a swing welding lathe. Operators must wear protective gear to shield against sparks and heat. A slight miscalculation could lead to injuries. Observing proper techniques takes practice and reflection. Users often learn from small mistakes, refining their skills over time. The journey involves both learning and creating.
| Dimension | Specification | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Swing Diameter | 32 inches | Maximum diameter of the workpiece that can be swung around the lathe. |
| Length of Bed | 120 inches | Total length of the lathe bed providing support for machining operations. |
| Max RPM | 500 RPM | Maximum speed of the spindle for welding operations. |
| Power Consumption | 15 kW | Amount of electrical power consumed during operation. |
| Control Type | CNC | Indicates that the lathe is controlled by a computer-based numerical control system for precise operations. |
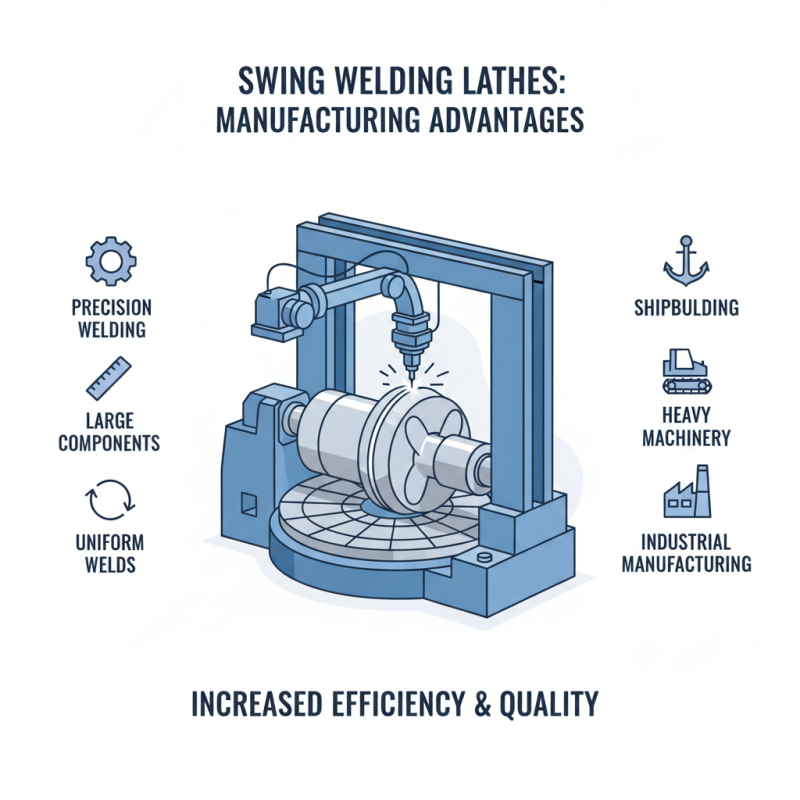
Swing welding lathes offer distinct advantages in manufacturing. They allow for precise welding of large components. The mechanism includes a rotating bed that supports heavy parts, facilitating uniform welding. This design is especially useful for industries like shipbuilding and heavy machinery.
The versatility of the swing welding lathe is remarkable. It accommodates various shapes, improving productivity. Welders can adjust angles easily, ensuring better access to difficult areas. However, operators must perform regular maintenance to maintain accuracy. Over time, wear can affect performance, requiring frequent checks.
Moreover, using swing welding lathes can reduce waste significantly. Their precise control minimizes over-welding and excess materials. Yet, operators need training to maximize efficiency. Understanding machine limits is crucial. Ignoring this can lead to costly errors. Balancing speed and quality is always a challenge in a fast-paced environment.
Swing welding lathes serve as versatile tools in various industries. Their design allows for the rotation of large workpieces, making them ideal for heavy fabrication tasks. According to industry reports, the global market for swing welding lathes is projected to grow at a CAGR of 4.5% through 2025. This growth is driven by increased demand in sectors like manufacturing and construction.
In the manufacturing sector, swing welding lathes are crucial for fabricating complex components. They can easily handle oversized plates and pipes. This capability enhances productivity and reduces lead times. A study noted that companies using swing welding lathes saw a 20% increase in efficiency. However, not every setup achieves optimal results. Improper alignment or inadequate skill can lead to flaws in welding, affecting the quality of finished products.
Moreover, swing welding lathes find applications in the aerospace and automotive industries. These sectors require precision and durability. The ability to weld thick materials in one rotation streamlines processes. Nevertheless, maintaining these machines can pose challenges. Routine checks and calibration are essential. Skipping these steps can result in costly repairs. This is a point of concern for many operators looking to maximize output while minimizing downtime.
This chart illustrates the percentage distribution of applications of swing welding lathes across various industries, highlighting their predominance in the automotive sector, followed by aerospace and energy sectors.